Managing administrative credentials is a critical part of hardening any Windows Server environment. One of the most common tasks for system engineers is to change Administrator password Windows Server wide, whether for security rotation, onboarding a new admin, or recovering access.
This technical guide explains how to change the Administrator password on Windows Server using Server Manager, Computer Management, PowerShell, Command Prompt, and the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE). All procedures follow enterprise-grade security practices and apply to Windows Server 2012, 2016, 2019, 2022, and newer releases.
Method 1 – Change the Administrator Password via Server Manager
This is the most common method for administrators logged in through RDP or the local console.
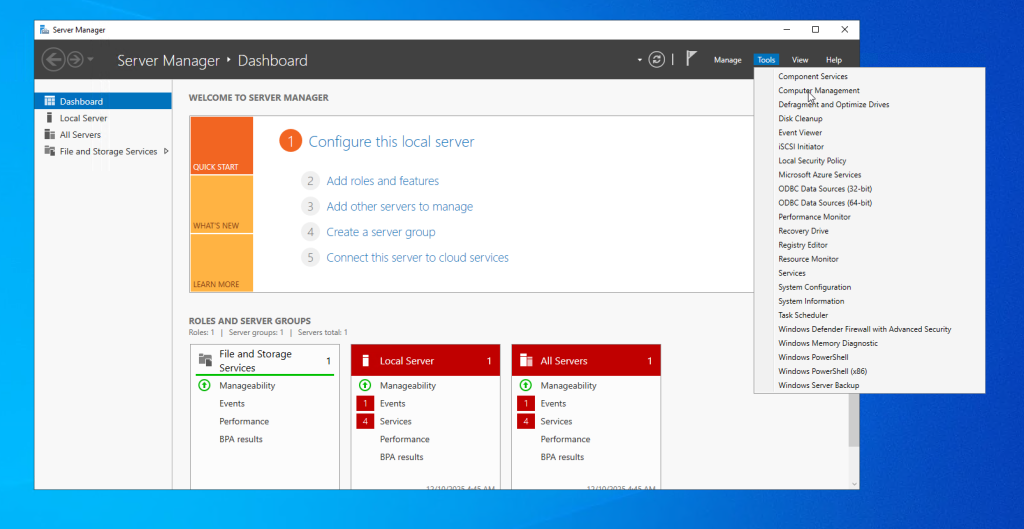
- Open Server Manager.
- Click Tools → Computer Management.
- Navigate to Local Users and Groups → Users.
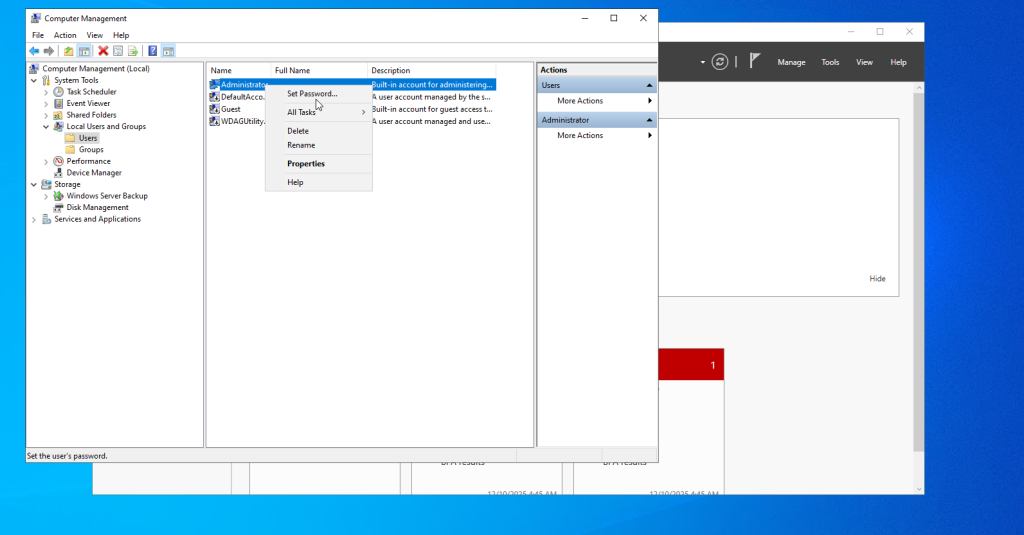
- Right-click Administrator → Set Password.
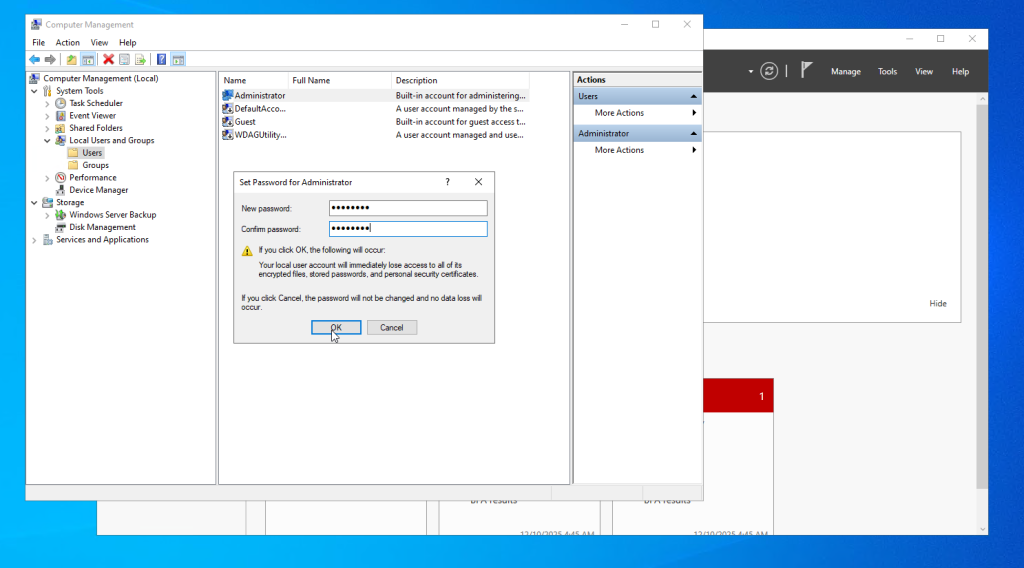
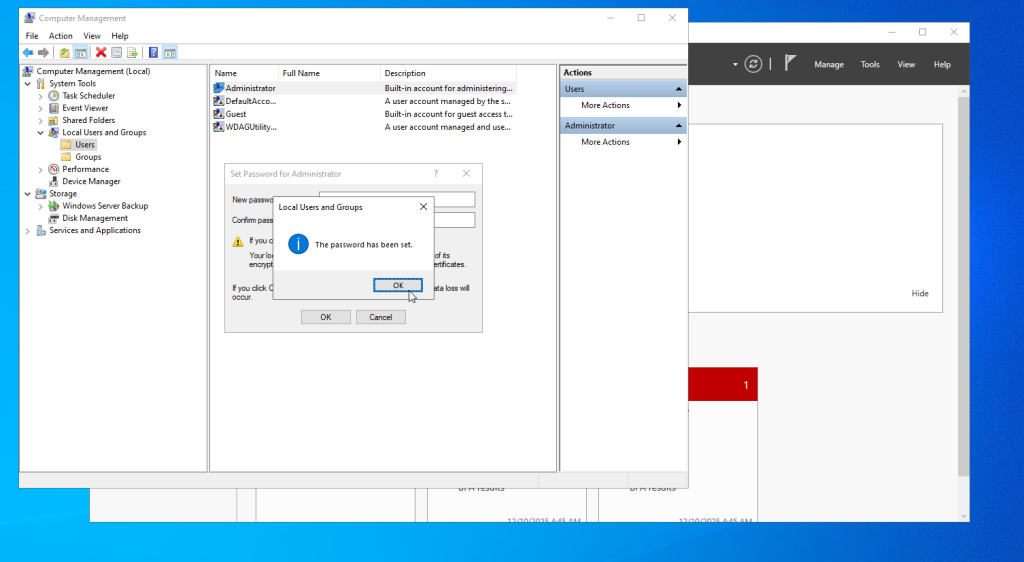
- Click Proceed and enter the new password.
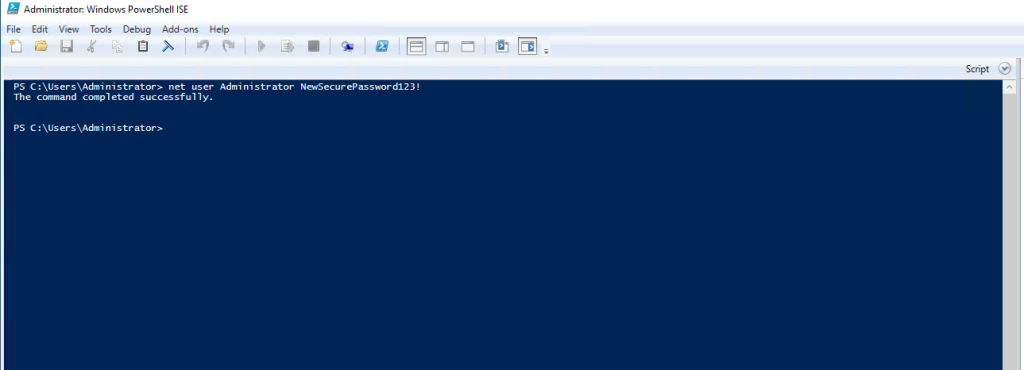
Method 2 – Change Administrator Password via PowerShell
PowerShell provides a fast, scriptable, and automation-ready method for updating the Administrator password.
Simple one-line password change
net user Administrator NewSecurePassword123!More secure PowerShell approach
$Password = Read-Host -AsSecureString
Set-LocalUser -Name "Administrator" -Password $PasswordMethod 3 – Change Administrator Password Using Command Prompt
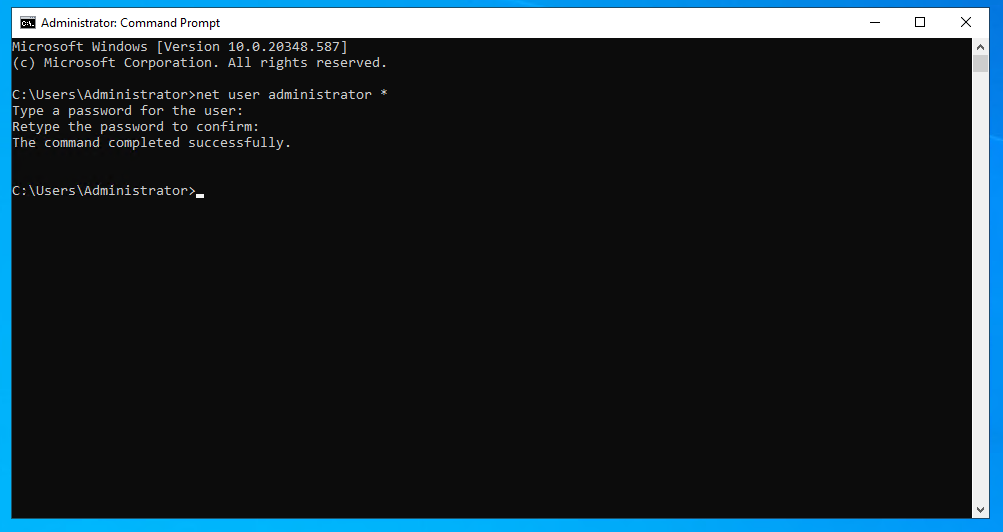
You can also use classic CMD commands to reset the Administrator password.
net user administrator *You will be prompted to securely enter and confirm the new password.
Method 4 – Reset Administrator Password from Windows Recovery Environment
This method is used when you lose full access to the server and need emergency recovery.
- Boot into Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE).
- Select Troubleshoot → Advanced Options → Command Prompt.
- Run the following command:
net user Administrator NewPassword123!Best Practices After Changing the Administrator Password
- Update the new password in your organization’s password vault or credential manager.
- Verify RDP access to ensure the change was applied successfully.
- Rotate administrative passwords periodically to meet security policy requirements.
- Disable the default Administrator account on domain controllers for improved security.
- Enable account lockout policies to prevent brute-force login attempts.
Conclusion
Changing the Administrator password on Windows Server is a vital security operation that protects systems from unauthorized access. Whether you update the password via graphical tools, PowerShell automation, Command Prompt, or recovery mode, following a structured process helps ensure a secure and compliant server environment.
By applying the methods and best practices in this guide, your Windows Server infrastructure will remain protected, stable, and ready for production workloads.